IoT Smart Grid
This code sample demonstrates how a SQL Server 2016 (or higher) memory optimized database could be used to ingest a very high input data rate and ultimately help improve the performance of applications with this scenario. The code simulates an IoT Smart Grid scenario where multiple IoT power meters are constantly sending electricity usage measurements to the database.
Contents
About this sample
Before you begin
Run this sample
Sample details
Disclaimers
Related links
About this sample
- Applies to: SQL Server 2016 (or higher) Enterprise / Developer / Evaluation Edition, Azure SQL Database
- Key features: Memory Optimized Tables and Table valued Parameters (TVPs), Natively Compiled Stored Procedures, System-Versioned Temporal Tables, Clustered Columnstore Index, Power BI Report
- Workload: Data Ingestion for IoT
- Programming Language: .NET C#, T-SQL
- Authors: Perry Skountrianos [perrysk-msft]
Before you begin
To run this sample, you need the following prerequisites.
Software prerequisites:
- SQL Server 2016 (or higher) or an Azure SQL Database
- Visual Studio 2015 (or higher) with the latest SSDT installed
- [Power BI Desktop Installed] (https://powerbi.microsoft.com/en-us/desktop/)
Azure prerequisites:
- Permission to create an Azure SQL Database
Run this sample
-
Clone this repository using Git for Windows (http://www.git-scm.com/), or download the zip file.
-
From Visual Studio, open the IoT-Smart-Grid.sln file from the root directory.
-
The sample includes two clients for generating the workload: ConsoleClient and WinFormsClient. Right click on either of these projects and select "Set as StartUp Project".
-
In Visual Studio Build menu, select Build Solution (or Press F6).
-
Modify the App.config Settings (located in the Solution Items solution folder)
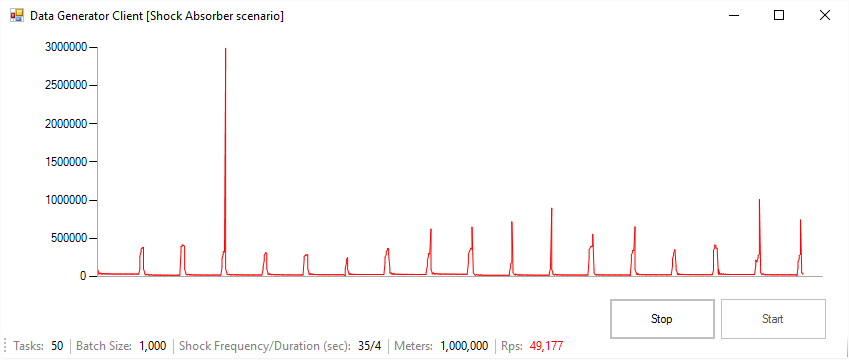
By accepting the default values for the following settings you should be able to see a data generated spike every 35 seconds with a 4 second duration. If you want to produce a continuous high data volume workload you should set the commandDelay to 0 and adjust the numberOfTasks and batchSize according to the hardware specifications of your environment.
- Db: SQL Server connectionString. Currently it is configured to connect to the local default SQL Server Instance using Integrated Security.
- insertSPName: The name of the Natively Compiled Stored Procedure that inserted the sample data. (Default Value: InsertMeterMeasurement)
- numberOfTasks: The number of Asynchronous Tasks the Data Generator uses. (Default Value: 50)
- numberOfMeters: The number of IoT Power Meters to be used. (Default Value: 1000000)
- batchSize: The sample data batch size.(Default Value: 1000)
- commandDelay: The delay between sql calls. Note that during a data generated spike the app changes this to 0. (Default Value: 1500ms)
- enableShock: Flag that turns on/off the data shock. This should be set to 0 for max high volume workload
- commandTimeout: SQL Command Timeout(Default Value: 600)
- shockFrequency: How often to generate a data spike. (Default Value: 35000ms)
- shockDuration: The duration of the data spike. (Default Value: 4000ms)
- rpsFrequency: The polling frequency for Rows per Second. (Default Value: 2000ms)
- logFileName: Log File Name. (Default Value: log.txt)
- powerBIDesktopPath: The local path to the PBIDesktop.exe. (Default Value: C:\Program Files\Microsoft Power BI Desktop\bin\PBIDesktop.exe)
-
Publish the Database
- Right click on the Db SQL Server Database Project and Select Publish.
- Click Edit... to choose your connection string.
- We recommend choosing PowerConsumption as the Database name as this is the default db name the sample is configured to run under.
- Click Publish.
- Note: For publishing to Azure SQL you need to 1. Change the DB project target platform to Microsoft Azure SQL Database V12 and 2. Comment the T-SQL in the mod.sql file in the Db/Storage folder before publishing.
-
Build the app and run it. Do not use the debugger, as that will slow down the app.
-
Start the workload
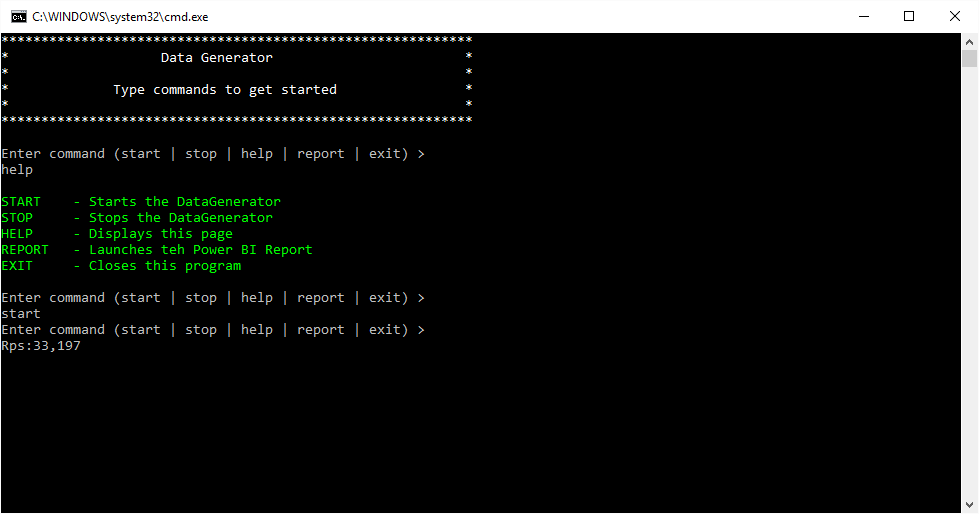
- From the ConsoleClient: Type 'START'
- From the WinFormsClient: Press the Start button.
-
Launch the Power BI Report
- From the ConsoleClient: Type 'REPORT' on the command prompt window.
- From the WinFormsClient: Click the Power BI Report link.
-
In the Power BI Desktop menu click on Edit Queries and then Source to make sure that both the Server and the Database Name match the values from Step 6. Click OK to apply changes.
Sample details
General Description
This code sample simulates an IoT Smart Grid scenario where multiple IoT power meters are sending electricity usage measurements to a SQL Server memory optimized database. The Data Generator, that can be started either from the Console or the Windows Form client, produces a data generated spike to simulate a [shock absorber scenario] (https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/dataplatforminsider/2013/09/19/in-memory-oltp-common-design-pattern-high-data-input-rateshock-absorber/). Every async task in the Data Generator produces a batch of records with random values in order to simulate the data of an IoT power meter. It then calls a natively compiled stored procedure, that accepts an memory optimized table valued parameter (TVP), to insert the data into an memory optimized SQL Server table. In addition to the in-memory features, the sample is leveraging System-Versioned Temporal Tables for building version history, Clustered Columnstore Index for enabling real time operational analytics, and Power BI for data visualization.
Visual Studio Projects:
- ConsoleAppClient: Console Data Generator client. Uses START | STOP | HELP | REPORT | EXIT commands.
- Data Generator: Data Generator client library. Uses multiple async tasks to produce a test data workload.
- Db: SQL Server Database project
- WFClient: Windows Forms Data Generator client.
Disclaimers
The code included in this sample is not intended to be a set of best practices on how to build scalable enterprise grade applications. This is beyond the scope of this quick start sample.
Related Links
For more information, see these articles:
- [In-Memory OLTP (In-Memory Optimization)] (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn133186.aspx)
- [OLTP and database management] (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/server-cloud/solutions/oltp-database-management.aspx)
- [SQL Server 2016 Temporal Tables] (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn935015.aspx)
- [In-Memory OLTP Common Design Pattern – High Data Input Rate/Shock Absorber] (https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/dataplatforminsider/2013/09/19/in-memory-oltp-common-design-pattern-high-data-input-rateshock-absorber/)
- [Power BI Download] (https://powerbi.microsoft.com/en-us/desktop/)