mirror of
https://github.com/Microsoft/sql-server-samples.git
synced 2025-12-08 14:58:54 +00:00
Token Authentication sample for Azure Active Directory
Contents
About this sample
Run this sample
Sample details
About this sample
The Token project contains a simple console application that connects to Azure SQL database using a self-signed certificate.
Software prerequisites:
- The
makecert.exeutility, which is included in the Windows SDK- It is sometimes included in Visual Studio installations (depending on the selections made during installation). A search of your machine for
makecert.exewould provide verification that the Windows SDK was installed. - If the Windows SDK was not installed, you may download it here
- You can learn more about the
makecert.exeutility here
- It is sometimes included in Visual Studio installations (depending on the selections made during installation). A search of your machine for
- PowerShell with Azure Active Directory Module
- To download the latest PowerShell version see this page
- Install the Azure AD PowerShell Module, if it is not already installed in your client machine.
Run this sample
-
Create an application account in Azure AD for your service.
- Sign in to the Azure management portal.
- Click on Azure Active Directory in the left hand navigation
- Click the directory tenant where you wish to register the sample application. This must be the same directory that is associated with your database (the server hosting your database).
- Click the Applications tab
- In the drawer, click Add.
- Click "Add an application my organization is developing".
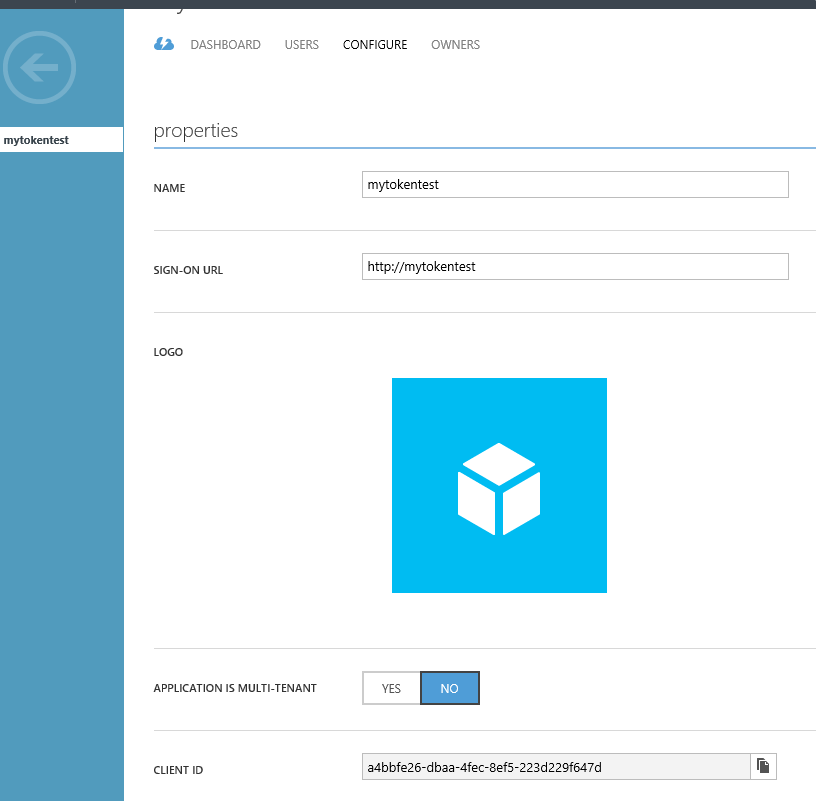
- Enter mytokentest as a friendly name for the application, select "Web Application and/or Web API", and click next.
- Assuming this application is a daemon/service and not a web application, it doesn't have a sign-in URL or app ID URI. For these two fields, enter http://mytokentest
- While still in the Azure portal, click the Configure tab of your application.
- Find the Client ID value and copy it into a text editor, you will need this later when configuring your application ( i.e. a4bbfe26-dbaa-4fec-8ef5-223d229f647d /see the snapshot below/)
-
Logon to your Azure SQL Server’s user database as an Azure AD admin and using a T-SQL command provision a contained database user for your application principal:
CREATE USER [mytokentest] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER- See this link for more details on how to create an Azure Ad admin and a contained database user.
-
On the machine you are going to run the project on, generate and install a self-signed certificate.
- To complete this step, you will need to use
Makecert.exe - Open a command prompt window
- Navigate to a folder where you want to generate a certificate file ( such as the folder where the demo files are) and change the following command for your environment
<Windows SDK Path>\makecert.exe -r -pe -n "CN=Cert_name" -ss My -len 2048 Cert_name.cerfor example, like so:
c:/"Program Files (x86)/Windows Kits/8.1/bin/x64"/makecert -r -pe -n "CN=mytokentestCert" -ss My -len 2048 mytokentestCert.cer - To complete this step, you will need to use
-
Add the certificate as a key for the application you created in Azure AD.
- Click the Microsoft Azure Active Directory Module for Windows PowerShell shortcut on desktop to open a Windows PowerShell workspace that has the Azure AD cmdlets.
- Copy the following code snippet to a text editor.
connect-msolservicewill ask for you Azure AD credentials. Please be sure to use credentials that are part of Azure AD global admin to connect and to proceed with the scripts below.
connect-msolservice $cer = New-Object System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Certificate $cer.Import("<full path>\Cert_name.cer") $binCert = $cer.GetRawCertData() $credValue = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String($binCert); New-MsolServicePrincipalCredential -AppPrincipalId "<client id>" -Type asymmetric -Value $credValue -Usage verify+ Replace <full path> with the path to your certificate and Cert_name with your Certificate name that you used in step 3 above. + Replace <client id> with the client ID you copied in step 1. + Copy and paste your snippet into the powershell window and run it.- The following command will verify that you added the certificate to your application's Active Directory Registration
Get-MsolServicePrincipalCredential –ServicePrincipalName "URL"-ReturnKeyValues 0
-
Configure the certificate and your application account in the app.config file in the project.
- In Visual Studio, open app.config in the Solution Explorer

- Find the app key
ida:Tenantand replace the value with your AAD tenant name (your AAD domain) - Find the app key
ida:ClientIDand replace the value with the Client ID for the application registration from the Azure Portal (the value from step 1). - Find the app key
ida:Cert_Nameand replace the value with the subject name (CN) of the self-signed certificate you created - For example:
<add key="ida:Tenant" value="cqclinic.onmicrosoft.com" /> //this is the AAD domain <add key="ida:ClientId" value="a4bbfe26-dbaa-4fec-8ef5-223d229f647d"/> //this is the Client ID <add key="ida:CertName" value="CN=mytokentestCert"/> //this is the Cert_name use by makecert.exe - Find the app key
- In Visual Studio, open Program.cs in the Solution Explorer

- Make the following changes:
builder["Data Source"] = "aad-managed-demo.database.windows.net"; // replace with your server name builder["Initial Catalog"] = "demo"; // replace with your database name
- In Visual Studio, open app.config in the Solution Explorer
-
Run the demo. (Click Run or press F5)
